The Definitive Guide to AI Image Prompting
Introduction: From Guesswork to Precision
Today, generative AI has placed a revolutionary new instrument into our hands. These tools can deliver fresh pictures in seconds, but without clear direction their output is a roulette wheel. The truly game-changing results don't come from hitting a "generate" button and hoping for the best, but from skillfully directing the technology to produce predictable, professional-grade, and context-aware visuals. This skill, a blend of architectural language and technical precision, is prompt engineering.
This guide is your comprehensive playbook. We will demystify the art and science of prompting, moving you from a passive user to an informed director of AI. First, we’ll explore the "why"—how these models interpret our words. Next, we'll survey the "what"—the 2025 toolkit of top image generators and their specific strengths in an architectural workflow. Finally, we will dive deep into the "how," deconstructing the anatomy of a master prompt and revealing the advanced techniques that will empower you to transform any design concept into a compelling, high-fidelity image.
The 'Why': Understanding the Digital Mind's Eye
Why does a long, detailed prompt consistently outperform a short, vague one? The answer isn't about feeding the AI more words for the sake of it. It's about understanding how these models "think" visually. To move from creating random pictures to directing precise architectural visualizations, we first need to look under the hood.
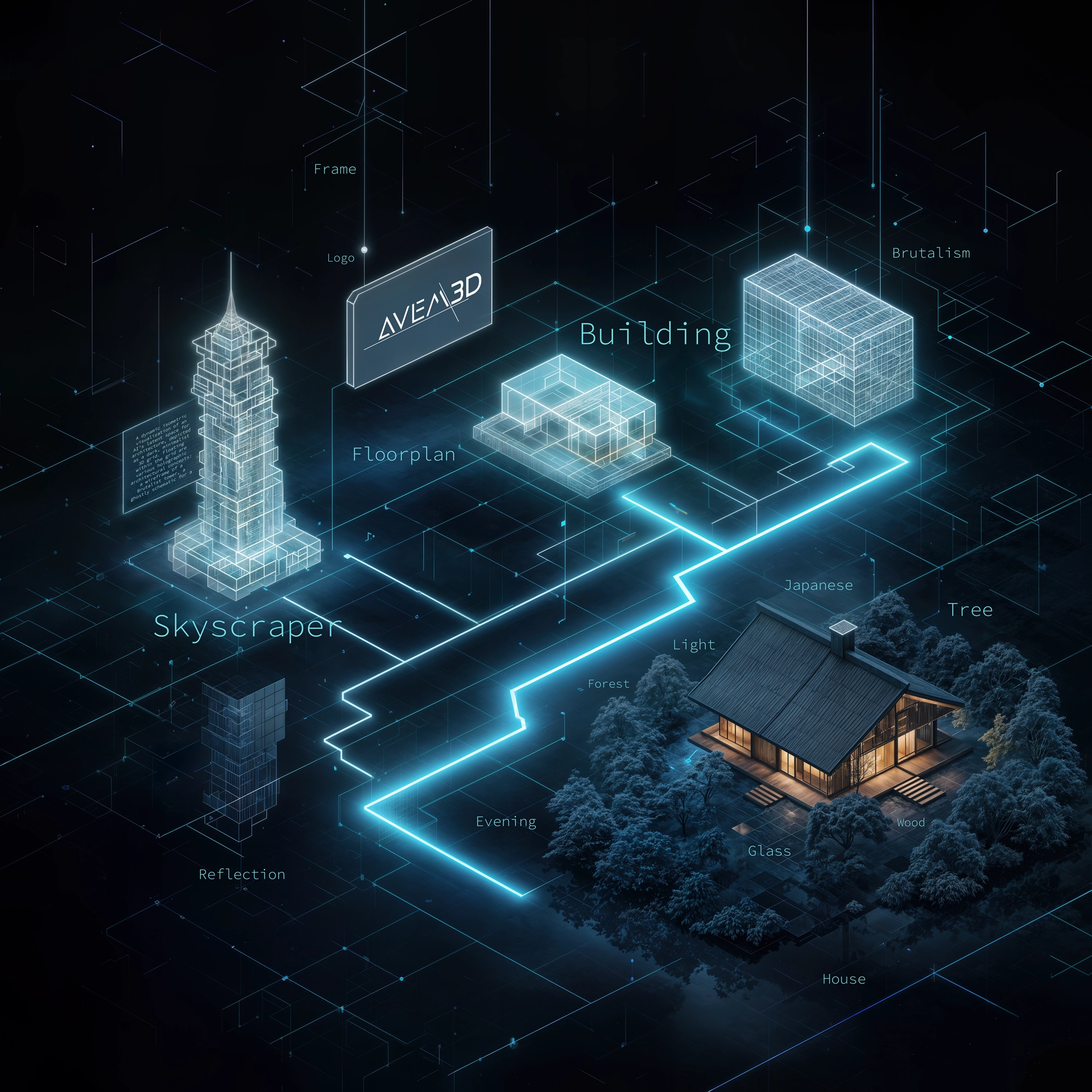
Imagine the AI starts with a canvas full of random static, like an old TV with no signal. Your prompt is the set of instructions it uses to turn that noise into a coherent image. Here’s how it works in simple terms:
First, the AI translates your words into a set of precise digital instructions (think of them as GPS coordinates for ideas). Then, the model begins to refine the static in a step-by-step process. At each step, it checks its work against your instructions, asking itself: "Does this emerging shape look like the 'Apartment complex' I was asked for? Does this texture I'm forming match 'rough-cast concrete'?".
This entire process happens within what’s called a latent space (a vast, multi‑dimensional map of every visual style, object, and concept the AI has ever learned). Your prompt's coordinates guide the AI to a specific destination on this map.
• A vague prompt like "a modern house" leaves the AI wandering in a huge, generic region of the map, resulting in an averaged, often uninspired, image.
• A long and specific prompt provides a precise location, guiding the AI-model exactly where to go. This is leading the AI to a much more focused and intentional result.
By understanding this fundamental relationship, you shift from making a hopeful request to giving a clear, technical briefing. You are directing the creative process, ensuring the final image is not a product of chance, but a direct reflection of your design intent.
The Toolkit: Choosing the Right Model for the Job
With a foundational understanding of how prompts work, the next step is choosing the right tool. The AI image generation landscape is evolving at a breakneck pace, but as of July 2025, four key players stand out for their power, flexibility, and relevance to architectural workflows.
1. Midjourney
Renowned for its exceptional artistic and cinematic quality, Midjourney is the go-to for early-stage conceptual design and mood boards. It excels at generating evocative and inspiring visuals with a distinct, illustrative style. Use it to explore formal or expressionist visual styles or to create high-end conceptual imagery that sparks client conversations, but expect less precise control over fine-grained details compared to other tools.
2. ChatGPT-4o (Integrated Image Generation)
The primary strength of OpenAI's latest model is its natural, conversational interface. This makes it ideal for rapid brainstorming, allowing you to refine images with simple follow-up requests like, "now make the cladding from weathered steel." It's best for generating a wide range of reference images or when speed is a higher priority than fine-tuned artistic control, as it lacks parameters for ensuring perfect consistency across a series.
3. Stable Diffusion
As an open-source model, Stable Diffusion is the power-user's choice for deep workflow integration and precision control. Its ecosystem of tools like ControlNet allows for high-precision renderings based on input sketches or CAD linework. Because it can be run locally, it's the most secure option for confidential projects. This flexibility comes with a steeper learning curve, but it is the unparalleled solution when custom visual styles and ultimate control are non-negotiable.
4. Flux AI
A powerful newcomer, Flux AI's architecture is built for high-fidelity output where accuracy and continuity are paramount. Benchmarks show its prompt-to-pixel accuracy rivals or exceeds its competitors. Its "Kontext" model is particularly relevant, allowing you to use reference images to maintain façade or character consistency while making precise local changes. With variants for cloud use or local hosting, it's an excellent choice for mid-to-late-stage visualizations, such as façade studies or stakeholder iterations where material changes must be tracked without reworking the entire scene.
The Anatomy of a Master Prompt: Core Building Blocks
Crafting an effective prompt is not about finding a single, elusive formula. Instead, it’s about using a flexible framework, assembling key components to transform a vague idea into a clear, actionable instruction for the AI. Understanding these core building blocks is fundamental to mastering AI-assisted design visualization. Each element adds a layer of specificity and control, allowing you to guide the AI with the precision of a design brief. Below are the five essential components of a master prompt for architectural visualization.
1. Subject & Content
This is the anchor of your prompt—the "what." It defines the primary focus of the image. A clear subject is the single most important element for a relevant result. Always start here.
• Simple: "A building"
• Specific: "A modern, single-family house with a flat roof and large cantilevered sections, featuring a central atrium and green terraces."
2. Style & Aesthetics
This component defines the visual language and emotional impact of the image. It's where you specify the design's heritage, the materials, and the desired rendering technique.
• Architectural Styles: Use keywords to guide the AI towards specific design movements.
Examples: Brutalist, Deconstructivist, Bauhaus, Japanese Minimalist, High-Tech, Art Deco.
• Rendering & Artistic Styles: Specify the desired final look and level of abstraction.
Examples: photorealistic, cinematic, schematic drawing, watercolor sketch, concept art, matte painting.
• Materials: Mentioning key materials is crucial for grounding the image in reality and conveying texture.
Examples: weathered steel, polished concrete, reclaimed timber, glass curtain wall, terracotta tiles.
3. Composition & Framing
This is where you direct the AI's "camera," dictating how the subject is presented to influence the viewer's perspective and focus.
• Camera Angles & Perspective: Control the vantage point.
Examples: eye-level view, bird's-eye view (aerial shot), drone shot, low-angle shot, isometric projection.
• Camera Shots: Define the proximity to the subject.
Examples: wide shot, medium shot, close-up, detail shot.
• Aspect Ratio: While often a separate parameter, mentioning the desired format in natural language can influence the composition.
Examples: "A wide 16:9 cinematic shot," or "A vertical 3:4 detail shot of the facade."
4. Lighting & Atmosphere
Lighting is pivotal for setting the mood, defining form, and enhancing realism. This component allows you to specify the time of day, weather, and quality of light.
• Time of Day & Natural Light: This has a dramatic effect on the mood and color palette.
Examples: golden hour, sunrise, midday, twilight, blue hour, night.
• Weather & Atmospheric Conditions: Add another layer of realism and emotion.
Examples: overcast sky, bright sunny day, foggy morning, dramatic storm clouds.
• Light Quality: Describe the nature of the light itself.
Examples: soft diffused light, strong directional light creating deep shadows, soft ambient interior lighting.
5. Technical Parameters & "Magic Words"
These are specific keywords and commands that influence the AI's rendering engine, pushing the output quality and detail to a professional standard.
• Output Quality & Detail: Signal your desire for a high-resolution, polished look.
Examples: 8K, 4K, ultra-high definition, intricate details, sharp focus.
• Render Engine Emulation: Prompt the AI to mimic the specific look and feel of popular rendering engines. This is a powerful trick for achieving photorealism.
Examples: Photorealistic, Architectural render, V-Ray, Cinematic lighting.
Conclusion: The Architect as AI Collaborator
Moving from a simple "generate" button to a structured, multi-faceted prompt is the key to unlocking the true potential of AI image generation. As we've seen, crafting a successful prompt is not about guesswork. It is a deliberate design process. By understanding the 'why' of latent space and choosing the right tool for the job, you can begin to direct the AI with intention.
The five core components (Subject, Style, Composition, Lighting, and Technical Parameters) are the building blocks of your new design brief. Think of them not as a rigid formula, but as a flexible framework for communicating your vision to a powerful new collaborator. Each keyword you choose, from "Wooden Facade" to "golden hour," helps steer the output from a random guess to a predictable and professional-grade visual.
This technology does not diminish the role of the architect, but elevates it. The creative vision, the understanding of space, and the specific design intent remain uniquely human. AI is the instrument, but you are the director. By mastering the art of the prompt, you can now translate your ideas into compelling, high-fidelity imagery with more speed, clarity, and creative freedom than ever before, ensuring your best work is not just imagined, but vividly and accurately seen.
Sources:
- [1] IBM Think. “What Is Latent Space? Understanding AI’s hidden representations.” (IBM Think)
- [2] Stable‑Diffusion‑Art.com. “How Stable Diffusion Works – a friendly overview of the latent‑diffusion process.” (Stable‑Diffusion‑Art)
- [3] Kaufman, J. WhyTryAI. “The Secret Sauce Behind DALL‑E 3: Why it’s freakishly good at following instructions.” (Kaufman, J. WhyTryAI)
- [4] VISO.ai. “Midjourney vs. Stable Diffusion: Which should you use?” (VISO.ai)
- [5] Benetou, F. “Midjourney 7: Everything you need to know.” fabienb.blog. (Benetou, F)
- [6] Flux AI. “Flux Kontext – product page.” (Flux AI)
- [7] The Economic Times. “Flux 1 Kontext & Playground API usher in in‑context editing workflow.” (The Economic Times)
- [8] DataCamp Tutorials. “Flux AI Image Generator: A guide with examples.” (DataCamp Tutorials)